When joining the military, you can expect many things to change in your life, and your health, to change rapidly.
One of the first things they will do is administer a round of vaccines to all recruits. This is vital to keeping everyone healthy.
You all have come from different states, and sometimes different parts of the world!
While that makes for an amazingly diverse group, it also means that diseases from around the world are all gathering in a single place.
Well talk about some of the vaccines you get right away, and then others that you will get yearly in the military.
Note: This military vaccine list is not comprehensive, and is subject to change at the behest of Department of Defense (DOD) requirements.
Table of Contents
Vaccines Received In Basic Training / Boot Camp
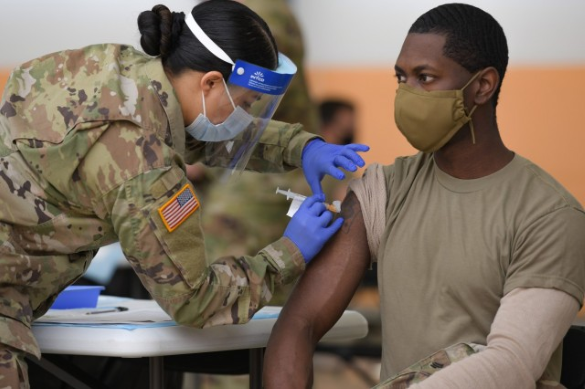
Here is a list of all the vaccines you will get right away in boot camp:
- Adenovirus, Types 4 and 7
- COVID-19 *
- Influenza (Flu Shot)
- Measles
- Meningococcal
- Mumps
- Polio
- Rubella
- Tetanus-diphtheria
- Varicella
Here’s a brief explanation of each:
#1. Adenovirus, Types 4 and 7
This is a live virus tablet given to prevent multiple forms of respiratory illness as well as asymptomatic infections in the tonsils, adenoids, and intestines of people.
The Adenovirus Type 4 and Type 7 vaccine has been shown to induce a durable antibody response.1
Possible adverse side effects:
Headaches, stuffy nose, sore throat, joint pain, nausea, abdominal pain, cough, diarrhea, and fever.
Related Article – Peanut Butter Shot: 5 Things You (probably) Didn’t Know
#2. COVID-19
No military vaccine list would be complete without the most important disease affecting our lives in recent years; COVID-19.
This vaccine drastically reduces the burden of COVID-19. It lowers the infection rates as well as the transmission of the disease.
There are several COVID-19 vaccines available, but the military issues the FDA-approved Pfizer-BioNTech/Comirnaty vaccine.
* The vaccine is no longer mandatory for every member serving in the US Military, Military Reserves, and National Guard. However, it is highly encouraged.
The COVID-19 vaccine has been extensively studied, and proven safe and effective through rigorous clinical trials.2
Possible adverse side effects:
Tiredness, headaches, muscle pain (around injection site), chills, fever, nausea, and exhaustion.
#3. Influenza (Flu Shot)
This shot is to prevent the seasonal outbreak of influenza. A special note about this one: a new vaccine is made twice a year to keep up with the constantly mutating disease.
You will be required to get this vaccine yearly, and the vaccine is available to veterans and military families.
With that said, it has been met with resistance in the past.3
Possible adverse side effects:
Mild fever, muscle pain, headache, bruising, malaise (general discomfort), and chills.
#4. Measles
This prevents the transmission and adverse effects of the measles disease. Untreated, it is highly contagious and results in an itchy rash of hives throughout the body. There are two doses needed of this vaccine, although it formerly was 3 doses.4
It is given in conjunction with the immunizations for mumps and rubella as the “MMR” shot.
Possible adverse side effects:
Fever, faint rash, headache, dizziness, and pain and stiffness in the joints.
#5. Meningococcal
This is a disease that affects the lining of your brain and spinal cord as well as causing bloodstream infections.
The Meningococcal vaccine is important because Meningococcal is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide.5
Possible adverse side effects:
Soreness, fever, chills, nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, and muscle/joint pain.
#6. Mumps
This vaccine prevents the full effects of measles. It is a two-dose vaccine and is good for an estimated 27 years.
It is given in conjunction with the immunizations for measles and rubella as the “MMR” shot.
Possible adverse side effects:
Soreness or swelling around the injection site swelling, rash, fever.6
#7. Polio
This prevents the disease that destroys the nerve cells in the spinal cord and creates paralysis in the body. One shot is adequate for a lifetime.
Possible adverse side effects:
Headache, abdominal pain, fever, diarrhea, and weakness.7
#8. Rubella
This disease is often spotted by its distinctive blotchy rash and is easily spread.
It is given in conjunction with the immunizations for measles and mumps as the “MMR” shot.
Possible adverse side effects:
Fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes and glands, and transient joint pain.8
#9. Tetanus-diphtheria
This prevents bacterial infections that cause painful muscle spasms and even death. Tetanus is usually contracted through a puncture of the skin. Diphtheria is spread from person to person.
You’ll need a booster Td shot in 10 years.
Possible adverse side effects:
Fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, headache, body aches, and soreness.9
#10. Varicella
More commonly known as the “Chicken Pox.” This is a highly infectious and irritating viral infection that causes itchy, blister-like rashes on the skin.
Possible adverse side effects:
Pain in the injection area, mild rash, back and joint pain, swelling, and headache.10
Related Article – Military Medical Waiver Guide
Vaccines Given Depending On Risk, Occupation, & Area of Responsibility

After basic training, you now go down the route specific to the contract you signed.
Your path is determined by your individual MOS, Rating, or AFSC. It includes locations in the world where you will be stationed and areas to which you may potentially deploy.
Here’s a list of other vaccines you may potentially have to take, depending on your path:
- Anthrax
- Cholera
- Haemophilus influenzae type B
- Japanese encephalitis
- Pneumococcal
- Smallpox
- Typhoid fever
- Yellow fever
#1. Anthrax
A serious bacterial disease that comes from sheep and cattle. Highly transferable, and has the potential to be weaponized because its spores are so resistant to destruction. This was a huge fear in the 1990s.
Who gets it?
This newer vaccine compound has been proven to be much safer than previous iterations. It is given to those who are deemed in need of it and will be going to the following AORs:
- USCENTCOM
- USINDOPACOM
- USNORTHCOM
Possible adverse side effects:
Muscle Aches, pain in the injection site, headache, and fatigue. This vaccine has a list of severe long-term side effects that are possible hence why it is only given when it is deemed absolutely necessary. Serious side effects include; autoimmune arthritis, lupus, infertility, allergic neuritis (which can lead to paralysis), nerve damage, and blindness.11
#2. Cholera
This is a bacterial disease of the small intestine and often leads to severe vomiting and diathermia. Infected water supplies are often the way it spreads.
Who gets it?
Anyone considered to be deployable and with the possibility of going to a third-world country.
Possible adverse side effects:
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, lack of appetite, and fatigue.12
#3. Haemophilus influenzae type B
This disease is a bacterial infection that can cause muscle stiffness, headaches, and even seizures. It is usually a danger to those under the age of 5.
Who gets it?
Those who will be traveling to third world countries where infection is a concern, or those who have not had the vaccine as a child.
Possible adverse side effects:
Pain, fever, chills, irritability, hives, sleepiness, loss of appetite, and swelling at the injection site.13
#4. Japanese encephalitis
This is a viral brain infection most commonly spread through mosquitoes and is most common in rural and agricultural areas.
Who gets it?
Those with orders to Asia, such as South Korea or Japan, or anywhere else in the Western Pacific, and those in the Special Operations field and III Marine Expeditionary Force.
Possible adverse side effects:
Low fever, chills, muscle pain, headache, nausea, and generalized rash.14
#5. Pneumococcal
This is a bacterial infection that can lead to many illnesses, including infections in the ear, sinuses, and bloodstream.
Who gets it?
This will be given when you are to be stationed or deployed anywhere outside of the continental United States.
Possible adverse side effects:
Pain, soreness, weakness, exhaustion, and hardening at the injection site.15
#6. Smallpox
The smallpox vaccine is available in very limited and controlled supply. The disease was announced as officially eradicated in 1980. This highly contagious disease was caused by the variola virus. This often fatal disease had flu-like symptoms along with a rash that left severe scarring.
While naturally occurring cases of the disease no longer appear, some theorize that the disease could be weaponized from frozen samples of live virus kept for research.
Because of this, the U.S. military ensured access to the vaccine after the attacks of 9/11.
More recently, the U.S. Army has developed a new smallpox vaccine. It will protect service members from any exposure to smallpox should it reoccur as well as the related disease, monkeypox.
Who gets it?
Only those who are deemed at risk of coming into contact with smallpox.
Possible adverse side effects:
Itchy, swollen lymph nodes, fever, headache, mild rash, muscle aches, and fatigue.17
#7. Typhoid fever
This is caused by a salmonella bacterial and you won’t feel the sickness until between 6 and 30 days after you have been infected. It causes flu-like symptoms with a high fever for several days.
Who gets it?
Those two weeks from being deployed or stationed outside the continental United States.
Possible adverse side effects:
Redness or swelling at the injection site, fever, general discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.18
#8. Yellow fever
The last shot on our military vaccine list is for yellow fever. Yellow Fever can cause illnesses ranging from aches and fever to severe liver disease with internal bleeding and the yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Who gets it?
Those who have the possibility of going to Africa, South America, or other areas flagged for high potential for yellow fever. Also, all Navy and Marine Corps personnel receive regular immunization.
Possible adverse side effects:
Headaches, muscle aches, low-grade fever, discomfort at the injection site, pruritus, and rash.19
References
- Collins ND, Adhikari A, Yang Y, et al. Live Oral Adenovirus Type 4 and Type 7 Vaccine Induces Durable Antibody Response. Vaccines (Basel). 2020;8(3):411. Published 2020 Jul 23. doi:10.3390/vaccines8030411 (source)
- Thomas SJ, Moreira ED Jr, Kitchin N, et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine through 6 Months. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(19):1761-1773. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2110345 (source)
- Burns VM, Castillo FM, Coldren RL, Prosser T, Howell RL, Kabbur MB. Perceptions of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Among U.S. Army Civilians and Dependents in the Kaiserslautern Military Community: A Mixed-Methods Survey [published online ahead of print, 2021 Feb 6]. Mil Med. 2021;usaa572. doi:10.1093/milmed/usaa572 (source)
- Griffin DE. Measles Vaccine. Viral Immunol. 2018;31(2):86-95. doi:10.1089/vim.2017.0143 (source)
- Myers TR, McNeil MM, Ng CS, Li R, Lewis PW, Cano MV. Adverse events following quadrivalent meningococcal CRM-conjugate vaccine (Menveo®) reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting system (VAERS), 2010-2015. Vaccine. 2017;35(14):1758-1763. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.02.030 (source)
- Sukumaran L, McNeil MM, Moro PL, Lewis PW, Winiecki SK, Shimabukuro TT. Adverse Events Following Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Vaccine in Adults Reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), 2003-2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60(10):e58-e65. doi:10.1093/cid/civ061 (source)
- Nzolo D, Ntetani Aloni M, Mpiempie Ngamasata T, et al. Adverse events following immunization with oral poliovirus in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of Congo: preliminary results. Pathog Glob Health. 2013;107(7):381-384. doi:10.1179/2047773213Y.0000000113 (source)
- Sukumaran L, McNeil MM, Moro PL, Lewis PW, Winiecki SK, Shimabukuro TT. Adverse Events Following Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Vaccine in Adults Reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), 2003-2013. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;60(10):e58-e65. doi:10.1093/cid/civ061 (source)
-
Regalado ME, Nieves Rodríguez B, Ghersy MT, Amilachwari M, Nieto JR, Velásquez G. Efectos secundarios de la vacuna contra difteria, tétanos y tosferina [Side effects of the vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus and whooping cough]. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 1990;47(5):295-303. (source)
-
Wise RP, Salive ME, Braun MM, et al. Postlicensure safety surveillance for varicella vaccine [published correction appears in JAMA 2000 Dec 27;284(24):3129]. JAMA. 2000;284(10):1271-1279. doi:10.1001/jama.284.10.1271 (source)
- Bower WA, Schiffer J, Atmar RL, et al. Use of Anthrax Vaccine in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, 2019. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2019;68(4):1-14. Published 2019 Dec 13. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr6804a1. (source)
-
Wiedermann G, Kollaritsch H, Jeschko E, Kundi M, Herzog C, Wegmüller B. Adverse events after oral vaccination against cholera with CVD103-HgR. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1998;110(10):376-378. (source)
- Moro PL, Jankosky C, Menschik D, et al. Adverse events following Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccines in the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System, 1990-2013. J Pediatr. 2015;166(4):992-997. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.12.014 (source)
-
Nothdurft HD, Jelinek T, Marschang A, Maiwald H, Kapaun A, Löscher T. Adverse reactions to Japanese encephalitis vaccine in travellers. J Infect. 1996;32(2):119-122. doi:10.1016/s0163-4453(96)91281-5 (source)
- von Elten KA, Duran LL, Banks TA, Banks TA, Collins LC, Collins LC. Systemic inflammatory reaction after pneumococcal vaccine: a case series. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(6):1767-1770. doi:10.4161/hv.28559 (source)
- Ertl HCJ. New Rabies Vaccines for Use in Humans. Vaccines (Basel). 2019;7(2):54. Published 2019 Jun 20. doi:10.3390/vaccines7020054 (source)
- Belongia EA, Naleway AL. Smallpox vaccine: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Clin Med Res. 2003;1(2):87-92. doi:10.3121/cmr.1.2.87 (source)
- Qamar FN, Yousafzai MT, Khaliq A, et al. Adverse events following immunization with typhoid conjugate vaccine in an outbreak setting in Hyderabad, Pakistan. Vaccine. 2020;38(19):3518-3523. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.03.028 (source)
- Lara AN, Miyaji KT, Ibrahim KY, Lopes MH, Sartori AMC. Adverse events following yellow fever vaccination in immunocompromised persons. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021;63:e13. Published 2021 Mar 1. doi:10.1590/S1678-9946202163013 (source)
- Ikon Pass Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big - January 31, 2025
- RTIC Military Discount: Find Out How To Save Big on Gear - January 30, 2025
- Traeger Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big on Smokers - January 28, 2025


