Though every single branch of the U.S. Military is extremely important and carries out tasks on a daily basis crucial to national security, there are a few elite forces that tend to receive more attention.
The 1st Special Forces Operational Detachment-Delta (1st SFOD-D), often shortened to Delta Force, is an example of one such elite special mission force.
The elite unit which also is referred to as Combat Applications Group (CAG) or Army Compartmented Element (ACE), operates under the division of the U.S. Army and operational control of the Joint Special Operations Command.
There is little surprise that many soldiers aspire to join what some members simply refer to as “The Unit”. It is tasked with handling some of the most dangerous and specialized missions in the world.
Related Article – Army MOS List: A List Of All 159 Army Jobs
CAG primarily deals with hostage rescue and counter-terrorism, as well as direct action and special reconnaissance work regarding “high-value targets”.
Due to the increased threat and focus on terrorism within the United States as well as abroad, the importance of ACE has only increased over the last couple of decades.
What does it take to join Delta Force?
Learn everything you need to know about what has been reported regarding this very complex, highly classified unit…
Jump To A Section
Brief History Of Delta Force

Delta Force is the primary counter-terrorism branch in the U.S. Military along with Navy SEAL Team Six, or DEVGRU.
In the history of United States military operations, members from both units have performed some of the most sophisticated, classified, and dangerous missions authorized by the U.S. National Command Authority.
Delta Force has origins that date back in America to the 1970s.
After a series of well publicized incidents occurred in the 70s, such as the Malayan Emergency and Grand Mosque seizure, the U.S. government decided to take action.
The U.S. Military launched the beginning of Delta Force as the first officially recognized, full-time counter-terrorism specialized force.
Colonel Charlie Beckwith was a key member in helping create CAG.
He reported his findings to the U.S. Military after serving with the British Special Air Service during the Malayan Emergency.
When he returned home Beckwith acknowledged that the U.S. Armed Forces could serve to benefit from a highly specialized unit.
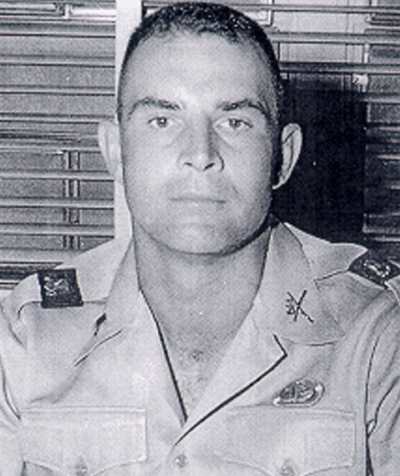

Beckwith’s now famous claim that the U.S. Military needed “not only teachers, but doers” led to the founding of Delta Force.
He envisioned extremely adaptable and entirely autonomous small teams that could operate with a broad array of skills in highly combative and risky situations.
The Pentagon launched Delta force in the mid-1970s as Beckwith estimated it would take another two years to fully prepare the new unit for specialized missions.
It was officially recognized on November 19, 1977.
Related Article: Top 20 Reasons to Join the Military (and 7 reasons not to)
Beckwith insisted on a long training period after being advised by John Watts from England who served as a Brigadier.
The intense scrutiny and training that advanced soldiers would need to complete the standards were released famously in what was labeled the “Robert Redford Paper”.
The paper outlines the historical precedents for becoming a part of CAG, many of which are still observed today in a four-phase selection and assessment process.
Colonel Bob “Black Gloves” Mountel was tasked with building the new unit after having already served on the 5th Special Forces Group.
Initial candidates were screened from volunteers in 1978.
By fall of 1979 they were granted permission by the U.S. Armed Forces to begin missions, infamously not long before the Iran hostage crisis.
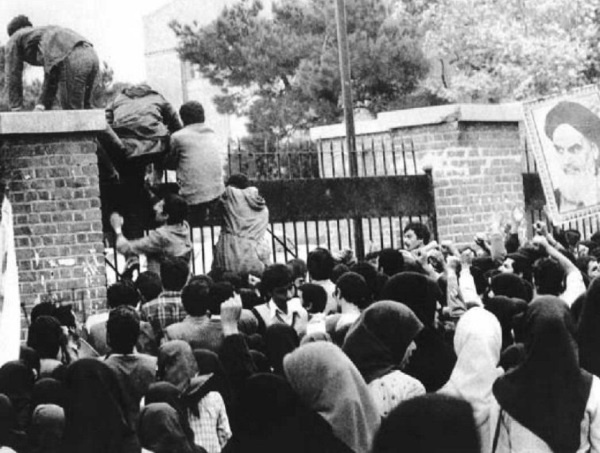

It was during this time in November of 1979 that Delta Force executed its first highly publicized mission, known as Operation Eagle Claw.
Operation Eagle Claw was ultimately aborted due to problems with helicopters, and turned out to be a real mess.

With that said, it quickly presented to the American government and people why the talented squad of soldiers was necessary for future American missions.
The U.S. government did reexamine its procedures after Operation Eagle Claw, and more soldiers were dedicated to counter-terrorism than before.
It gave way to the eventual rise of Navy SEAL Team Six, which was founded by commander Richard Marcinko.

The Joint Special Operations Command was also created as the organizational and control department for all counter-terrorist units in the U.S. Military.
Related Article – US Army Grooming Standards
Delta Force Selection

Today, the majority of Delta Force operatives are selected from a pool of U.S. Army Special Operations Command’s elite Special Forces Group (aka Green Berets) as well as the 75th Ranger Regiment.
Related Article – Green Berets Vs. Rangers: 5 Major Differences
There’s been speculation that some soldiers are also considered from other special operations units of the U.S. Military, such as Marine Force Recon, Air Force Pararescue (PJ’s), and even Air Force Combat Controllers.
With that said, there’s no way to to determine that with certainty.
All in all, Delta Force selection is considered one of the most intense and challenging of any elite force in the U.S. Armed Forces considering that candidates looking to join are already members of other specialized units.
Therefore, it is impossible to become a part of “The Unit” immediately after enlisting.
Soldiers are carefully selected from a narrow pool after having proved themselves, sometimes for years.
Delta Force and DEVGRU are thus considered lofty ambitions for soldiers that want to make a career out of the U.S. Military.
It is one of the most highly sought after units so it goes beyond just skills but also reputation while serving in other units and word of mouth from commanding officers.
Initial Screening / Requirements

The U.S. Army has actively recruited for Delta Force though it does not necessarily define it by the official title.
It has used other tactical terms to describe an “elite, specialized unit” considering new applicants.
Notices tend to state initial signup requirements for consideration like:
- Must be male in gender.
- Must be 21 years or older.
- Classified in grade of E-4 through E-8.
- Classified in grade of O-3 captains or 0-4 majors for officer positions.
- Received a high enough score on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery.
- At the time of application have at least two and a half years of service remaining.
Related Article – Army Ranks and Pay
Though the exact requirements for Delta Force are not heavily reported since it is such a classified organization, there are some known additional requirements for considering to attend a briefing on admission.
These include:
- Candidates must be airborne qualified, or having volunteered for airborne training.
- Candidates must be eligible for a security clearance level of “Secret”.
- Never convicted by court-martial or have disciplinary action placed in their official military personnel file.
The vast majority of what we know about CAG is based on the reporting found in Eric Haney’s book “Inside Delta Force”.
Haney, who managed to cover the discreet force in unprecedented detail.

According to Haney, the selection for Delta Force begins with a physical endurance test.
Candidates must meet requirements regarding:
- Push-ups
- Sit-ups
- Inverted crawl
- 100 meter swim (fully dressed)
- 2 mile run
Candidates must also endure a series of land navigation courses that push the boundaries of every conceivable human condition from a physical, mental, and emotional standpoint.
Prospective operatives reportedly undergo an 18 mile all-night land navigation while beginning with a 40 lb. rucksack.
The weight of the rucksack increases as well as the length of the course over repeated marches.

Haney reports that the final course of physical testing ends with a 40 mile trek carrying a 45 pound rucksack over the rough terrain.
The time needed to clear the test has not been reported.
Regardless, that’s an increase of 22 miles and 5 pounds respectively when you compare the first march to the last one.
Qualifying soldiers are also tested from psychological point of view.
The exams are intended to weigh if a candidate is mentally prepared enough to handle the complicated and remarkably serious missions new members will be expected to carry out after training is completed.
Candidates are expected to go through a board of Delta instructors, psychologists, and a Delta commander in order to face a series of questions.

All of these tasks are completed in order to just be approached regarding the opportunity to get selected for Delta’s Operator Training Course (OTC).
The demanding six month training teaches a variety of counter-terrorism and counterintelligence techniques.
Related Article: 6 Ways To Check If Someone Was In The Military / Verify Military Service
During OTC, recruits are expected to maintain little to no contact with friends and family.
They will also receive advanced firearm and other weapon training.
According to one former CAG operator, for those that get the rare opportunity to attend OTC the attrition rate is high.
Additionally, the Committee on Armed Services reported in 2006 that nearly three-fourths of all Delta operators originate from the 75th Ranger Regiment.

While most of those that advance in the Delta Force selection process will continue with CAG, the Central Intelligence Agency Special Activities Division (SAD) also receives some recruits from Delta Force.
Delta Force Training

1st Special Forces Operational Detachment-Delta receives highly specific training. It is originally conducted during the aforementioned Operator Training Course, or OTC.
OTC will help verify that recruits are capable of lasting with the elite force and involves some very detailed training over approximately six months.
Since Delta Force remains a confidential unit, not everything about OTC is known for sure, with much of the information being speculated upon.
Once again, Eric Haney and his book “Inside Delta Force” details the vast majority of what we know about Delta Force training.
Haney reports that new recruits will learn about marksmanship, demolitions and breaching, combined skills, tradecraft, and executive protection.

Marksmanship receives a huge focus.
Trainees are expected to have extremely high accuracy rates.
According to Haney they begin with stationary targets before progressing to moving targets. Then, tactical rooms are setup for hostage takeover situations.
Delta Force operators also train to become highly skilled demolition and breaching experts. They learn how to pick virtually all types of locks, not only on buildings but cars and safes too.

They also learn how to make bombs with common materials and other advanced demolition techniques.
The FBI and FAA, as well as other federal government agencies work closely with new operatives during OTC training to present methods for dealing with terrorists and hostage situations.
Hostage situations are therefore presented in a number of different locations from big buildings to aircraft or ships.
Along with being highly prepared and knowledgeable hostage experts, Delta Force also trains members to become skilled in espionage.
Thus, skills like “dead drops”, brief encounters, load and unload signals, surveillance, and counter-surveillance are all reportedly taught to trainees.

A major first training requirement of Delta Force when it was first launched back in the 1970’s was to teach members an advanced number of driving scenarios.
Often these advanced defensive and offensive driving courses are taught at Camp Peary, often referred to as “The Farm” by CIA insiders.
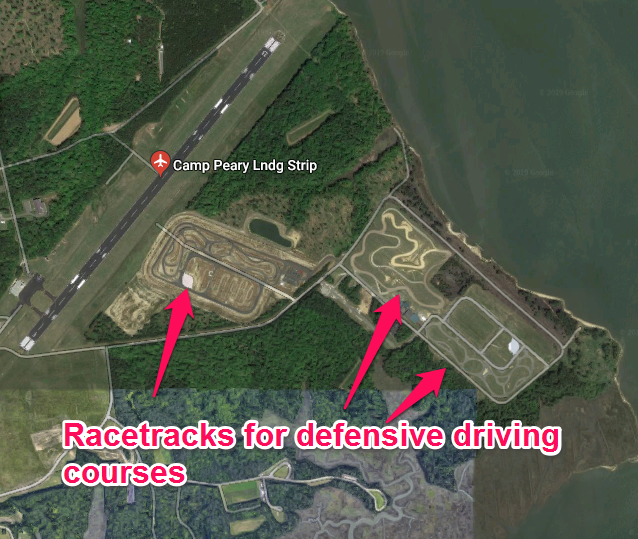
Related Article – CIA Special Activities Division (SAD): 12 Things You Never Knew
Therefore, they are also highly trained and knowledgeable operating a number of different vehicles and weapons.
The U.S. Secret Service and DSS reportedly works with Delta Force during these training exercises.
Haney concludes that Delta Force OTC training concludes with a culmination exercise.
It reportedly tests the students ability to apply everything they learned from training in one complicated, highly detailed final exercise.
Delta Force Vs. SEAL Team 6 (DEVGRU)

Delta Force is frequently compared to U.S. Navy SEAL Team 6 (DEVGRU) and rightfully so. The two elite forces have several comparisons and often operate together.
DEVGRU was created as a result of Delta Force and has followed many of its methods closely.
Delta Force & DEVGRU Similarities
- They both primarily deal with counter-terrorism and hostage situations.
- They both currently only have male members.
- The basic entrance requirements are similar including needing to be 21 years or older as well as having previous combat experience.
- The physical testing standards are reportedly similar.
Delta Force & DEVGRU Differences
- Delta Force members must have already been in airborne training. SEALs need similar training but also take it a step further with advanced skydiving.
- DEVGRU recruits undergo SERE training. Delta Force candidates do not during OTC.
- DEVGRU forces are ranked slightly differently and also draft new recruits to their team.
- The two elite forces have reportedly been involved in some notoriously famous secretive missions, as well as separate ones from each other.
Related Article: Delta Force vs. Navy SEALs
Delta Force Weapons and Equipment
U.S. Delta Force is well recognized for being some of the most advanced specialists in the world when it comes to training regarding a number of different vehicles, equipment, and weapons.
What is really wild about Delta Force is they actually have their own distinct team of gunsmiths that develop weapons specially for the specialized ops unit first.
Therefore, Delta Force weapons are highly customized with personal adjustments that account for everything from the stock and grips, to sights and other moving parts.
Delta Force is responsible for introducing weapons like:
- The M3a1 Grease Gun
- Walther MP
- Colt Commando
- M16
- Colt M4/M4A1
- Beretta M9
- Glock 9mm pistol
- HK MP5
- HK416 Carbine
- Colt M1911a1 .45 pistol
In terms of operational equipment, little surprise that Delta Force also knows how to use and regularly operates some of the U.S. Military’s most advanced and sophisticated machinery.
Related Article – Navy SEAL Weapons and Gear: 24 Rifles, Handguns, Shotguns, and More
Some of the most popular CAG vehicles include:
- Ground Mobility Vehicle (GMV)
- GMV 1.1
- Desert Patrol Vehicle
- Interim Fast Attack Vehicle (IFAV)
- Ranger Special Operations Vehicle (SOV)
- Lightweight Tactical All Terrain Vehicle (LTATV)
- M1161 Light Strike Vehicle
- Non-standard Tactical Vehicles (NSTV)
- LMTV Special Ops ‘War Pig’
- Pinzgauer 6×6 Vehicle
- RG-31 MRAP
- RG-33 MRAP
- Armored Ground Mobility System (AGMS)
- Stryker Infantry Carrier Vehicle (ICV)
- Rescue All Terrain Transport (RATT)
Notable Delta Force Members

Delta Force (CAG) has several noteworthy members. As you would expect, it is the elite of the elite so every operator that joins its prestigious ranks is very highly decorated.
However, these former members stand out:
- Colonel Charles A. Beckwith, founder of Delta Force
- Dale Comstock, former Delta Operator & author
- Eric L. Haney, former Delta Operator & author
- Gary Gordon, former operator and MoH recipient
- Randall Shughart, former operator and MoH recipient
- Mike Vining, former Delta operator
Quick Frequently Asked Questions
What is Delta Force?
1st Special Forces Operational Detachment Group, commonly known as Delta Force, is the US Army’s elite special mission unit tasked with hostage rescue and counter-terrorism.
What branch is Delta Force?
While Delta Force is technically a branch of the US Army, they are a part of the Joint Special Operations Command, or JSOC.
How can you join Delta Force?
In order to join Delta Force, you first need to enlist in the Army and serve in the capacity of a special operations soldier. Potential Delta Force recruits are usually selected from the Green Berets, as well as the 75th Ranger Regiment.
How many Delta Force members are there?
According to some estimates, there are as many as 250 – 300 operators serving in a direct action and hostage rescue capacity.
When was Delta Force founded?
Founded by Colonel Charlie Beckwith, it was officially recognized on November 19, 1977.
Conclusion
Delta Force is clearly one of the most advanced units in the U.S. Armed Forces.
These extraordinarily trained soldiers are prepared to handle a number of dangerous hostage or terrorist situations.
Joining the ranks of CAG is very challenging and only a very small pool of U.S. Military members are ever considered for the elite unit.
We can rest easier at night knowing these highly trained individuals continue to watch after our well-being as they handle high stakes terrorism missions.
References:
- https://www.military.com/special-operations/delta-force.html
- https://nationalinterest.org/blog/buzz/us-armys-delta-force-how-secret-group-deadly-soldiers-came-be-55057
- https://www.goarmy.com/special-forces/qualifications-and-benefits.html
- https://thenewsrep.com/43573/surviving-delta-force-selection-assessment-pt-1/
- https://beta.deltaforceops.com/members/
- Ikon Pass Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big - January 31, 2025
- RTIC Military Discount: Find Out How To Save Big on Gear - January 30, 2025
- Traeger Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big on Smokers - January 28, 2025






Wasn’t Jerry Boykin involved in the founding of Delta? I’ve heard that for a long time yet his name is nowhere listed as being an original in its conception … I know he was in the Delta team but if anyone can clarify I would really appreciate it, thank you