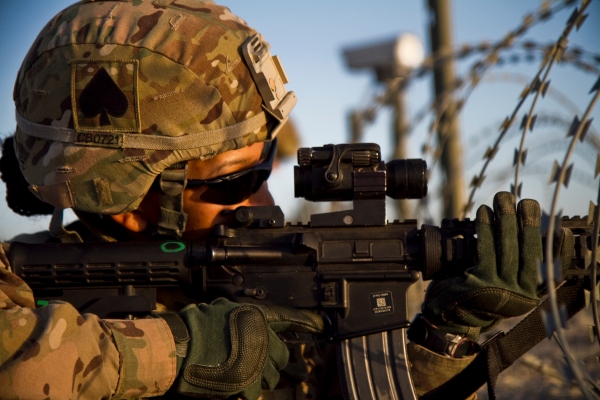
When you think of the U.S. Army, probably the first job you think of within the branch is an Army Infantryman – MOS 11B.
Army Infantrymen (11B) are the main land combat force, and are known as “Eleven Bravo.”
The incredibly important role in the U.S. Army is responsible for defending the country through real-life combat.
Soldiers also act in the mobilization of vehicles, weaponry, troops, and more.
Related Article: Marine Machine Gunner (MOS 0331): Job Description And Summary
Jump To A Section
Education, Qualifications, and Training

Before you get started, it is important to determine right off the bat if you want to become a U.S. Army Infantryman 11B or Indirect Fire Infantryman 11C.
The 11X recruiting program is designed to pipeline Army Basic Training to the Army Infantry training program.
The 11X program challenges new recruits with the option of becoming MOS 11B or MOS 11C.
There is a higher demand for MOS 11B, and reports indicate the position makes up 15-17% of the U.S. Army.
Related Article – 5 Best Combat Jobs In The US Navy
Education
There is no guarantee that recruits going through the 11X – Infantry Enlistment Option will become MOS 11B.
You have to earn it, so hard work during your education and training is extremely important.
The minimum education needed to become a U.S. Army Infantryman (11B) is a high school diploma or GED.
Additionally, you must complete a Combat (CO) ASVAB score of 87.
The ASVAB is short for “Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery,” which is a series of tests that help you better understand your strengths in the U.S. Military.
The higher the score on the ASVAB, the better your odds of becoming MOS 11B.
Qualifications
Training to become MOS 11B is open to both men and women.
There are a number of standards and qualifications you need to meet to become MOS 11B, especially since the Army expanded its OSUT training in 2019.
Now, there are additional weapon qualifications including handling M4 rifles, M240 machine guns, and M249 squad automatic weapons.
No high-security clearance is required to become an Army Infantryman.
Soldiers must meet a “very heavy” strength requirement and physical profile requirement of 111221.
Correctable vision must be 20/20 in one eye, and 20/100 in the other eye.
Color Vision discrimination for MOS 11B is red/green.
Related Article – Air Force Combat Controller (CCT) (1C2X1): Career Details
Training
Training for an Army Infantryman consists of two sections: Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training.
The job training for 11B requires 22 weeks of One Station Unit Training (OSUT) which is a combination of 10 weeks in boot camp and 12 weeks in AIT spent in the classroom and in the field.*
Basic training and advanced job training are combined into a single course.
OSUT training takes place at Fort Moore (formerly Fort Benning), in Georgia.
*The U.S. Army recently expanded upon its Infantry Training in 2019 to introduce more combative courses, lifesaver courses, day and night land navigation, and different weapons qualifications.
What does an Army Infantryman Do?

Army Infantrymen are the main land combat force and are considered the backbone of the U.S. Army.
Infantrymen must protect the country against any threat by land.
They are responsible for capturing, destroying, and repelling enemy ground forces.
Fire Team Member
Since U.S. Army Infantrymen are the primary land defense for the branch of the military they regularly participate in shooting drills.
As a member of a fire team, you can expect to test your skills handling day and night shooting with several Army stables including M4 rifles, M230 machine guns, and M249 automatic weapons.
The Army continues to build upon its training for fire team members with more time in the field, including tactical training that focuses more on squad formations.
Land navigation is also a point of emphasis for U.S. Army Infantrymen.
Soldiers also learn basic combative training including hand-to-hand combat and tactical combat casualty care (TCCC).
Related Article – Marine Corps Infantry Assault (MOS 0351): Career Details
Combat & Reconnaissance Missions
As an Army Infantryman, you will likely see time in combat.
Infantrymen serve in combat operations and reconnaissance missions.
When you assist in reconnaissance operations, you can expect to “employ, fire, and recover anti-personnel and anti-tank mines, locate and neutralize mines, operate, mount/dismount, zero, and engage targets using night vision sight.”
Additionally, you may lead an infantry team in combat missions “providing tactical and technical guidance to subordinates and professional support to both superiors and subordinates in the accomplishment of their duties.”
U.S. Army Mobilization
During times of combat, it is not uncommon to mobilize troops, vehicles, and weaponry.
As a result, Army Infantrymen 11B are trained to conduct mobilization in a variety of settings on land.
During training, you will spend close to a week on vehicle platform training.
Soldiers that are assigned to Bradley or Stryker units also must learn how to drive and perform maintenance on their assigned vehicles.
During mobilization in the military, it is not uncommon to have skills associated with landmine warfare, anti-armor techniques, urban terrain, squad tactical training, as well as the operation of M203 grenade launchers.
Related Article – Army Combat Engineer (MOS 12B): Career Details
Prisoners of War (POWs)
One result of combat is dealing with prisoners of war, with Army Infantrymen being the first means to process POWs.
It is an important role of MOS 11B, and just one of their many responsibilities.
In addition to handling and processing POWs, an Army Infantryman might also need to evaluate terrain and select weapon emplacement.
Communications
Army Infantrymen are experts in both weaponry and machinery, so there is a need to maintain and store combat weapons of all types.
Infantrymen must know how to operate and maintain communications equipment including radio.
There is a demand to know how to operate in an NBC-contaminated area as well as construct field expedient firing aids.
Additionally, soldiers might record operational information on maps.
Infantrymen must know how to receive and implement combat orders, and direct deployment of personnel in a number of different operation types (offensive, defensive, retrograde, etc).
During combat, soldiers need to request, observe, and adjust direct supporting fire.
All of these tasks for MOS 11B are not possible without excellent communication skills as well as an advanced understanding of the terrain, methods of warfare, and combat strategies.
Additional Skills
There are a few other skills that are not mandatory yet go a long way in proving what makes an excellent U.S. Army Infantryman 11B:
- Terrific Physical Condition: Soldiers are placed in a number of different settings, some of them extreme, and they must be able to survive off the land. Therefore, high demand for peak physical conditioning is necessary.
- Interpersonal Skills: Once again communication is vital. Infantryman work as a member of a fire team. Each role is essential and the ability to work as part of a team is mandatory.
- Open Mind: Things change in combat all of the time. Soldiers need to keep an open mind and be able to adjust to new challenges, which often happen organically while in the field.
- Stress Management: It should be obvious that infantrymen face challenges not common to ordinary people. As a result, soldiers need to know how to manage stress as well as perform well in high-stress situations such as direct combat.
Related Article – Marine Corps Tow Gunner (MOS 0352): Career Details
What does an Army Infantryman make?

The U.S. Army features the same base pay regardless of job within the military.
However, you may receive bonuses for deployments, retention, and for family separation. You’ll also receive pay increases with higher rank and more years of service.
The longer you serve in the U.S. Army, the more you will make.
You can follow the pay table below to figure out what you can expect to make based on U.S. Army rank for Infantryman MOS 11B:
| Insignia | Pay Grade | Rank | Abbreviation | Minimum Monthly Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-1 +4 months | Private | PVT | $1,917.60 | |
| E-2 | Private Second Class | PV2 | $2,149.20 | |
| E-3 | Private First Class | PFC | $2,259.90 | |
| E-4 | Specialist | SPC | $2,503.50 | |
| E-4 | Corporal | CPL | $2,503.50 | |
| E-5 | Sergeant | SGT | $2,730.30 | |
| E-6 | Staff Sergeant | SSG | $2,980.50 | |
| E-7 | Sergeant First Class | SFC | $3,445.80 | |
| E-8 | Master Sergeant | MSG | $4,957.20 | |
| E-8 | First Sergeant | 1SG | $4,957.20 | |
| E-9 | Sergeant Major | SGM | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Command Sergeant Major | CSM | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Sergeant Major of the Army | SMA | $6,055.50 |
Benefits
The U.S. Army has several benefits included with a monthly salary:
- Medical Insurance
- Vacation Time
- Retirement
- Special Pay
- Housing: Allowances for living expenses, utilities, and maintenance.
- Food: Allowance for the on-base dining hall and access to tax-free department and grocery stores.
- Education: Army members can earn full tuition, merit-based scholarships, allowances for books and fees, plus an annual stipend for living expenses.
It is also worth noting that you could earn up to $41,000 in cash bonuses for enlisting under certain Military Occupational Specialties.
The special military bonus is reserved for particular in-demand or highly-dangerous positions.
Related Article – Marine Corps Scout Sniper (MOS 0317): Career Details
Job Reviews
U.S. Army infantrymen overwhelmingly have positive things to say about the military career choice.
According to Indeed.com, most Infantrymen claim “pay and benefits” and “job security and advancement” as the two best features of the job.
Also, many Infantrymen like the “culture” of the military job as well as management opportunities.
The lowest-rated category on Indeed for Army Infantrymen is “work-life balance” which makes sense as having a family while serving in the U.S. Armed Forces is far from easy.

Joining the U.S. Army has an overall rating of 4.4 out of 5 stars on Indeed.com, which is about as good as you will find on the career website.

Civilian Job Opportunities
There are a number of civilian job opportunities for an Army Infantryman (11B) following discharge from the U.S. Military.
Many of the skills you learn while in the U.S. Army are universal to just about every type of job.
Infantrymen are renowned for being great at handling high-stress situations and are often natural-born leaders.
There are no civilian occupations that are the direct equivalent of an Army Infantryman MOS 11B.
Regardless, several civilian jobs are comparable such as:
- Security Guards: Employed in just about every industry with starting salaries at $28,500.
- Training and Development Specialists: A more niche job with higher pay starting at $60,900 for some companies.
Army PaYS Program
Soldiers should consider enrolling in the Army PaYS program following retirement.
The PaYS program is a recruitment option that guarantees a job interview with military-friendly employers following retirement.
“Military-friendly” employers are known for being large corporations that seek experienced and trained veterans for the skills they attain while in the U.S. Army.
The Army currently lists AT&T, Hewlett-Packard, Kraft Foods Global, Sears Holdings Corporation, Time Customer Service, and Walgreens as partners of PaYS and great employers for Army Infantryman post-service.
Related Article: Army Height And Weight Standards
Frequently Asked Questions
Does an Army Infantryman (MOS 11B) see combat?
Army Infantrymen (MOS 11B) are the main land combat force, known as “Eleven Bravo.” These personnel are responsible for defending the country through real-life combat.
Can you choose between 11B and 11C in the Army?
As an Infantryman, you may be listed as an MOS 11X. Army Infantryman 11B are riflemen, while Indirect Fire Infantrymen 11C carry mortar weapons systems. The needs of the Army will dictate which MOS you’re assigned.
How long is AIT for MOS 11B?
The training for Army Infantrymen 11B consists of Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training (AIT), for a total of 22 weeks.
How many MOS 11B are in the Army?
As of July 2019, the Army had 19,820 11B infantrymen on active duty. The Infantry makes up approximately 15 to 17% of the Army’s total force.
Does the Army Infantry get paid more?
Like all military branches, the Army pays soldiers according to rank and time in service. However, Infantrymen may be eligible for bonuses, including an enlistment incentive of up to $40,000.
Summary
U.S. Army Infantrymen MOS 11B have many duties and responsibilities.
The job title is the epitome of the U.S. Army, as you are the primary means of attack and defense on land for the military.
You will become a member of a fire team, which could result in deployment to one or more dangerous settings involving direct combat.
Additionally, you will learn to handle a large volume of weapons, military vehicles, as well as Prisoners of War (POWs).
There is also training provided on advanced land navigation (day and night) as well as opportunities for leadership positions that are extremely beneficial both in the Army and with future civilian opportunities.
Resources:
- https://www.goarmy.com/careers-and-jobs/browse-career-and-job-categories/combat/infantryman-11b.html
- https://www.indeed.com/cmp/U.S.-Army/reviews?fjobtitle=Infantryman
- Ikon Pass Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big - January 31, 2025
- RTIC Military Discount: Find Out How To Save Big on Gear - January 30, 2025
- Traeger Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big on Smokers - January 28, 2025





