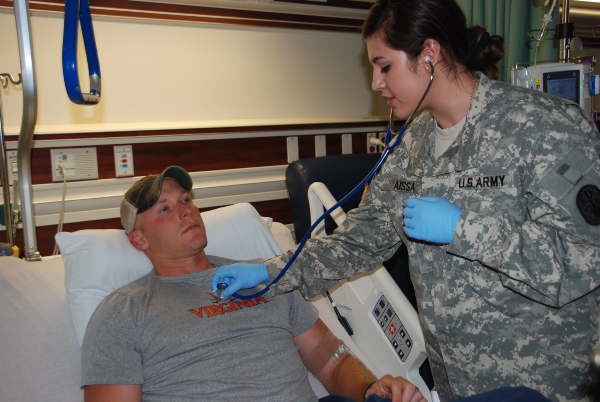
Cardiovascular medicine is anything that has to do with the heart or blood vessels.
An Army Cardiovascular Specialist (MOS 68N) serves that same purpose in a clinical setting yet as part of the U.S. Armed Forces.
Army Cardiovascular Specialists treat soldiers dealing with cardiovascular problems as well as assist in preventive care.
Learn more about what it takes to become an Army Cardiovascular Specialist (MOS 68N) by reading the entire article.
Education, Qualifications, and Training
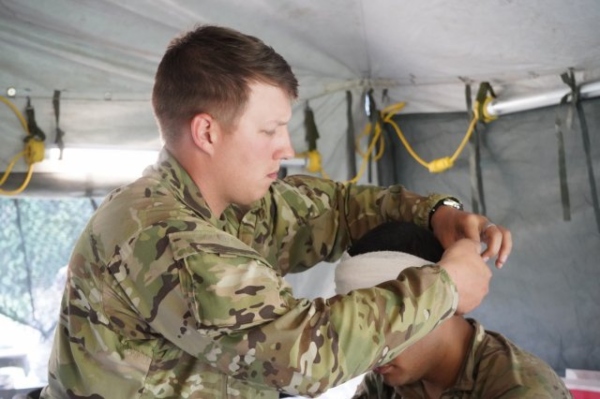
Army Cardiovascular Specialists (MOS 68N) assist or manage cardiac clinics as they perform specialized examinations and tests.
Due to the significance of the issues they handle there is a good deal of education and training required to perform this role in the U.S. Army.
Related Article: Army Height And Weight Standards
Education
Education is vital to becoming an Army Cardiovascular Specialist.
First, you need to complete high school.
The Army recommends taking advanced courses in biology, chemistry, algebra, and general science.
It also helps to have some secondary education under your belt like taking classes at a community college, or even having an Associate’s or Bachelor’s degree.
However, it is not mandatory in order to become 68N MOS.
What is mandatory is that you complete the Armed Services Vocational Battery Test (ASVAB).
Service members that wish to become an Army Cardiovascular Specialist must score at least General Technical (GT): 107 as well as Skilled Technical (ST): 101.
Qualifications
The Army has listed off some helpful tips for becoming MOS 68N, in addition to obtaining specialized education related to cardiovascular diseases and treatments.
For starters, it serves you well to have an extreme attention to detail given the serious issues you are dealing with in a medical setting.
Additionally, the ability to communicate effectively is important.
So is a natural ability to work under stressful situations.
Lastly, the best Army Cardiovascular Specialists have a willingness to care and help others given the nature of their work.
Training
After completing Basic Combat Training (BCT) for 10 weeks you can progress into specialized training related to 68N MOS.
Advanced Individual Training (AIT) is where Army recruits spend time focusing on their Military Occupational Specialty (MOS).
AIT for Army Cardiovascular Specialists is broken down into two phases.
The first phase takes place at Fort Sam Houston in Texas and lasts 21 weeks.
Phase two consists of even more specialized training and lasts about 35 weeks.
The location for phase two training can take place at a variety of forts across the United States.
You will learn how to perform cardiac tests and examinations.
The Army will also train you on how to assist physicians in other areas related to cardiovascular health.
What does an Army Cardiovascular Specialist Do?
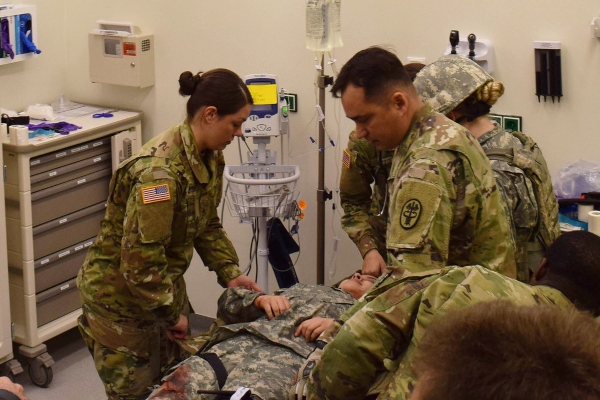
Army Cardiovascular Specialists (MOS 68N) assist in activities at cardiac clinics.
Cardiovascular health is centered on the heart and surrounding blood vessels.
The exact duties can vary from day-to-day though there are some common tendencies.
Related Article – Army Counterintelligence Agent (MOS 31L): Career Details
Job Duties of 68N MOS
A Cardiovascular Specialist assists physicians with the management of cardiac clinics in Army settings.
Your patients are current service members that need assistance with their cardiovascular health.
You will perform specialized, invasive and non-invasive cardiac tests and examinations on patients.
Other job duties include:
- Performing diagnostic echocardiography studies.
- Assisting with the diagnosis and intervention of catherizations.
- Performing and recording tests related to diagnostic data of the heart.
What does an Army Cardiovascular Specialist make?

The Army pays its service members based on years of service and rank.
Consequently, your Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) is not important in terms of pay.
The Army offers outstanding benefits including free housing and food.
Additionally, you could receive a higher salary for performing very well on the ASVAB prior to beginning training for MOS 68N.
The Army can also help with advancing your higher learning education with scholarships and other allowances.
| Insignia | Pay Grade | Rank | Abbreviation | Minimum Monthly Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-1 +4 months | Private | PVT | $1,917.60 | |
| E-2 | Private Second Class | PV2 | $2,149.20 | |
| E-3 | Private First Class | PFC | $2,259.90 | |
| E-4 | Specialist | SPC | $2,503.50 | |
| E-4 | Corporal | CPL | $2,503.50 | |
| E-5 | Sergeant | SGT | $2,730.30 | |
| E-6 | Staff Sergeant | SSG | $2,980.50 | |
| E-7 | Sergeant First Class | SFC | $3,445.80 | |
| E-8 | Master Sergeant | MSG | $4,957.20 | |
| E-8 | First Sergeant | 1SG | $4,957.20 | |
| E-9 | Sergeant Major | SGM | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Command Sergeant Major | CSM | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Sergeant Major of the Army | SMA | $6,055.50 |
Benefits
The U.S. Army has several benefits included with a monthly salary:
- Medical Insurance
- Retirement
- Vacation Time
- Special Pay
- Education: Army members can earn full-tuition, merit-based scholarships, allowances for books and fees, plus annual stipend for living expenses.
- Housing: Allowances for living expenses, utilities, and maintenance.
- Food: Allowance for the on-base dining hall and access to tax-free department and grocery stores.
Job Reviews
Indeed.com has job reviews for Medical Specialists of the Army which is helpful in determining if MOS 68N is right for you.
You can also find jobs after completing your time with the U.S. Army at job sites like GlassDoor.com.
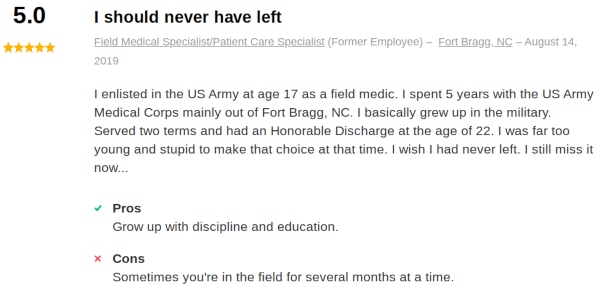
Beginning your clinical work in the U.S. Army can lead to further opportunities down the road while you advance your education.

Related Article – US Army Grooming Standards
Civilian Job Opportunities
The civilian job outlook for an Army Cardiovascular Specialist (MOS 68N) is very bright.
Medical jobs will continue to be in high demand following your time of service in the Army with direct civilian job equivalents.
Those that served as 68N generally advance to working in a hospital, clinic, nursing home, or rehabilitation center following discharge.
Army retirees traditionally work as Medical Assistants, Cardiovascular Technicians, and Physician Aides.
Summary
Joining the Army to become a Cardiovascular Specialist (MOS 68N) is a good way to get direct experience as well as further your education if you so choose.
There are many ex-military that would not be working the civilian career they do now had the Army not supported their education as well as provided real world experience.
Resources:
- https://www.goarmy.com/careers-and-jobs/browse-career-and-job-categories/medical-and-emergency/cardiovascular-specialist.html
- https://www.indeed.com/cmp/U.S.-Army/reviews?fcountry=ALL&fjobtitle=Medical+Specialist
- Ikon Pass Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big - January 31, 2025
- RTIC Military Discount: Find Out How To Save Big on Gear - January 30, 2025
- Traeger Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big on Smokers - January 28, 2025