It’s a certainty that future battles will not only be fought on the battlefield but they will also be fought in Cyberspace.
That concerns Air Force commanders greatly because many Air Force weapons and command and control systems are directly tied to computer use.
Rest assured that America’s enemies are well aware of this fact too.
That’s why protecting America’s military computers and the cyberspace that they operate in is paramount to America’s success in any future war.
That is where Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Personnel come into play.
They are the Air Force members that take the lead in keeping cyber threats away from Air Force and other military computer systems.
The importance of this task cannot possibly be emphasized enough as America becomes more and more dependent on computer systems to gain an edge in future battles.
Related Article – Air Force Geospatial Intelligence (1N131): Career Profile
More on this critical US Air Force career field can be seen here in this YouTube video:
Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Requirements and Qualifications
If you are interested in becoming an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist, you will first have to fulfill all of these prerequisites before you can enter into training in this career field.
ASVAB Requirements
Any of the four combinations below are required to enter the Cyber Defense Operations career track:
- Minimum ASVAB Score of 55 on Electrical, 57 on the Electronic Data Processing Test (EDPT), and 60 on Cyber
- A minimum ASVAB score of 64 on General and 57 on EDPT
- A minimum score of 54 on General, 60 on Cyber and 57 on EDPT
- A score of 60 on Electrical and 57 on EDPT
Additional Qualifications
- Be between the ages of 17 and 39
- Possess a high school diploma or GED
- Have normal color vision and depth perception
- Be able to lift 40 lbs.
- Prior knowledge of information systems is preferred by not required
- Successful completion of 7.5 weeks of Air Force Basic Military Training held at Joint Base Lackland in San Antonio, TX (Not required of those with prior military experience or training)
• Completion of a current Single Scope Background Investigation (SSBI) that leads to the ability of an Airman being granted access to Top Secret or similar level material
Training and Career Path to Become an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist
It takes much training to make sure that Air Force Cyber Defense Operations personnel are capable of keeping military computer networks and online communications safe and secure.
Here is the training path it takes to become qualified to perform the duties of an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist.
Related Article: 5 Best Coast Guard Jobs
Air Force Technical Training Information

Technical training for this Air Force career field takes place at Keesler Air Force Base outside of Biloxi, Mississippi.
It lasts approximately three and a half months long, although this can vary depending on class availability.
During this time, a new recruit will learn the basics of Air Force computers, networks, and information systems and start to learn how to better protect them.
This will include such things as gaining knowledge and proficiency in using Air Force information systems and learning about their capabilities, technical protocols, and functions.
The Airman will also learn about networked Air Force information systems, computer network information flow, and their associated support components.
The new Cyber Defense Operations recruit will also learn how to solve information system operation problems and learn what resources are at their disposal to secure Air Force information systems and to correct possible breaches of them.
On-the-Job Training
As with most Air Force jobs, the main core of learning for an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist is done with hands-on training.
This will take place at the new recruits’ first permanent duty assignment.
During this training phase, the Airman will learn how to maintain and secure the specific Air Force information systems that they will be working with.
It most likely will take any Cyber Defense Operations airman several months of on-the-job training to become proficient enough at their job to function in their job on their own.
Related Article – Air Force Cyber Warfare (1B4X1): Career Details
How Much Are Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialists Paid?
All military members, regardless of their branch of service, are paid according to their rank and time in service.
Most new Air Force Cyber Defense Operations recruits will start out as an Airman Basic (E-1).
Those with prior computer system knowledge or IT training may be bumped up to Airman (E-2) or Airman First Class (E-3) ranks.
| Insignia | Pay Grade | Rank | Abbreviation | 2023 Minimum Monthly Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-1 +4 months | Airman Basic | AB | $1,917.60 | |
| E-2 | Airman | Amn | $2,149.20 | |
| E-3 | Airman First Class | A1C | $2,259.90 | |
| E-4 | Senior Airman | SrA | $2,503.50 | |
| E-5 | Staff Sergeant | SSgt | $2,730.30 | |
| E-6 | Technical Sergeant | TSgt | $2,980.50 | |
| E-7 | Master Sergeant | MSgt | $3,445.80 | |
| E-8 | Senior Master Sergeant | SMSgt | $4,957.20 | |
| E-9 | Chief Master Sergeant | CMSgt | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Command Chief Master Sergeant | CCM | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Chief Master Sergeant Of The Air Force | CMSAF | $6,055.50 |
Other forms of pay and incentives may include such things as:
• Housing allowance for those that live off base (BAH)
• Subsistence allowance (Food – BAS)
• Temporary duty pay
• Hazardous duty pay
• Cost of living incentives
• Tuition reimbursement
Of course, all healthcare needs for Air Force members are always covered 100%.
What’s Life Like as an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist?
So what exactly do Cyber Defense Operations Specialists do in the Air Force?
The list is long and contains many variables that relate directly to an Airman’s permanent duty station.
Here is a list of the responsibilities that come with being an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist:
- Cyber Defense Operations personnel ensure that Air Force and other military computer networks and online communications are kept secure; this includes the deterrence, detection, and elimination of cyber threats and attacks.
- Constantly conduct Air Force IT system risk and vulnerability assessments
- Points out weaknesses in Air Force IT and related online communication systems and makes timely recommendations for improvement.
- Makes sure that new and existing Air Force computer systems and related lines of communication are always kept in compliance with military security standards and protocols.
- Conduct audits of cybersecurity incidents to determine why they occurred and how to better prevent such incursions in the future; this will include follow-up procedures and the conducting of IT forensic investigations.
- Constantly stay aware of current Air Force IT system policies and protocols and keep up to date on the latest and best cybersecurity techniques.
- Undergo constant training and learning that enables them to defend Air Force computer systems and related online communications from any potential cyber threats.
Whenever you work in a job that entails keeping computer information systems and their associated message flow secure, you will be working in a challenging and sometimes stressful environment.
You will, however, be working in a more comfortable office-style setting most of the time.
This is true even when working on more remote sites because computers and their associated support equipment need to be kept cool.
Although you may have to go on temporary duty assignments periodically as an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist, most of the time you will be stationed on a base where you can have your family with you too.
That makes this a better-than-average military occupation for those that have families.
Related Article – Military Child Care: 8 Great Options
Job Reviews
Those that have performed the duties of an Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialist say it’s a faced-paced and challenging job.
Most seem to like it despite the obvious drawbacks of working with constantly changing and evolving IT systems.
Here is what a few former Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialists had to say on the website indeed.com about their experience working in this Air Force career:
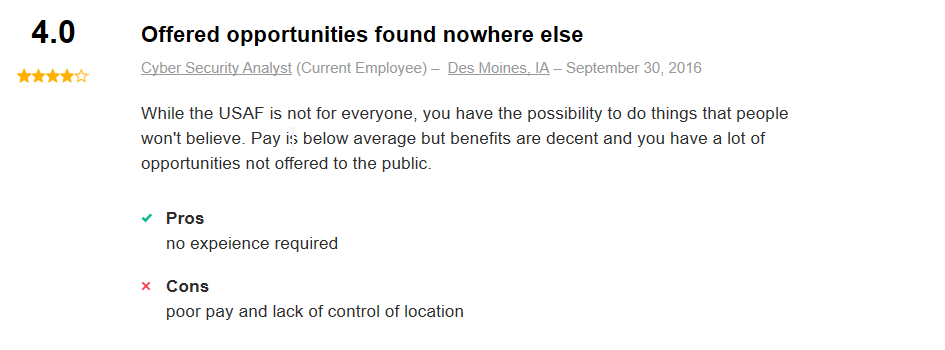
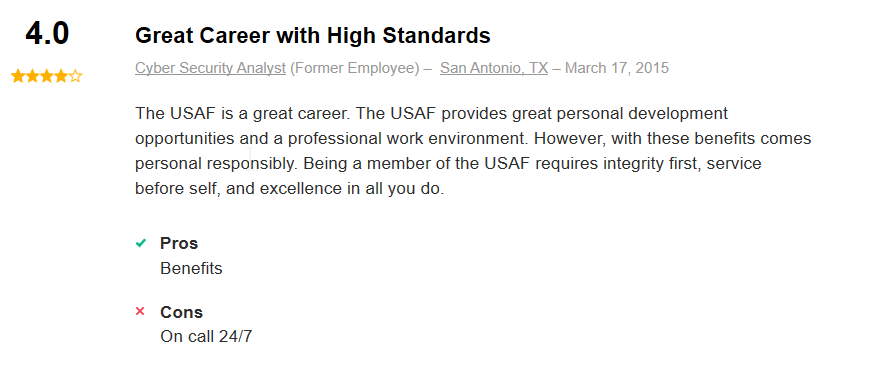
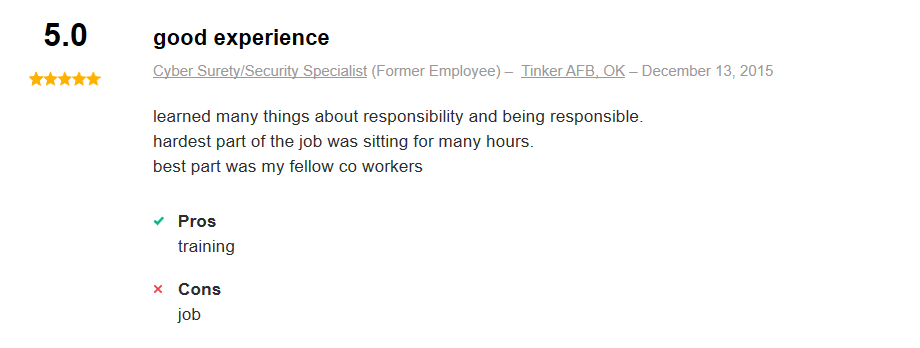
Related Article – Air Force Aviation Resource Management (1C0X2): Career Profile
Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Civilian Career Opportunities
Anytime you have the ability to work with computers and keep them secure, you are very unlikely to ever find yourself without a job.
That is certainly the case with former Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialists.
Each year computer systems worldwide seem to face more and more security threats.
That makes the skills Ex-Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialists possess in high demand in the job marketplace.
Almost every business these days relies greatly on the computer and information systems found inside them and recognizes the need to keep them safe from cyber threats.
Here are some typical jobs that those with Air Force Cyber Defense Operations skills usually qualify for:
- Cybersecurity analyst
- Computer inspection and cyber compliance specialist
- Network security specialist
- Cyber Surety and Information Assurance
- Risk management analyst
- IT quality assurance analyst
- Nuclear surety evaluator
These are some companies that are known to hire former Air Force Cyber Defense Operations Specialists:
- ISHPI Information Technologies, Inc. (DBA ISHPI) – Portsmouth, VA
- Systems Planning and Analysis – Offutt AFB, NE
- US Department of the Air Force – Andrews AFB, MD
- VMware – Broomfield, CO
- Bechtel – Pueblo, CO
- BAE Systems – Hill AFB, UT
- WestRock – Atlanta, GA
Many civilian cybersecurity jobs have excellent starting salaries that are oftentimes in excess of $60,000/year or more.
According to the Department of Labor, the median salary of an Information Security Analyst in 2022 was $112,000.
Those that land jobs as government cyber surety contractors will also have their military time count toward retirement.
Related Article – 10 Best Air Force Jobs For Civilian Life
References:
Official Air Force Recruiting Page
Air Force Reserve Official Page
- 5 Worst Jobs in the Air Force - June 20, 2024
- 4 Steps For Visiting An Air Force Recruiter Near You - June 19, 2024
- Air Force Safety Specialist (1S0X1) - June 19, 2024
General FAQ
What is cyber surety in the Air Force?
Air Force Cyber Surety specialists work to prevent, detect, and counter cyber attacks against USAF computer systems. Similar to cyber security, they ensure computer networks and online communications remain secure.
How long is tech school for cyber surety?
Tech school for Air Force Cyber Surety takes place at Keesler AFB, Mississippi, and lasts about two months.
What ASVAB score do you need for cyber security?
To qualify as an Air Force Cyber Surety specialist, you’ll need to score 64 on the General portion or 54 on General and a 60 or better on the Cyber Skills portion of the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB).
How much does Air Force Cyber Surety pay?
Like all USAF jobs, pay is commiserate with rank and time in services. A new airman, with less than two years in service, can expect to make a base pay of $1,733 per month plus benefits.
How hard is it to get int cyber security in the USAF?
To enter the Air Force Cyber Surety field, you’ll need a Top Secret security clearance, which means passing a background check scrutinizing your criminal, financial, and health records.

