Air Force Aerospace and Operational Physiology (4M0X1) personnel provide pilot and crew members will all of the necessary tools to safely handle an emergency.
These Airman are highly trained individuals who have taken on the task of preparing airman for any extreme circumstances that might come their way during a flight.
Education, Qualifications and Training
Education
Air Force Aerospace and Operational Physiologists must have a High School Diploma or GED with 15 college credits.
It is preferred that the individual completed high school biology and chemistry courses.
Individuals must meet the minimum ASVAB requirements for the Air Force.
The requirements for the ASVAB test will change depending on if a High School Diploma or GED is obtained.
Related Article – Joining The Military After College: How To Do It The “Right” Way
Qualifications
You have to be between the ages of 17 (with parental consent-18 without) and 39 to qualify for this position.
Individuals must have a thorough understanding of aerospace.
They must complete and gain an understanding of aerospace-related courses.
Recruits are required to have a clear voice without speech impediments.
As an individual or as a team, the recruit must be able to perform aerospace and operational physiology duties.
Training
After completing 8.5 weeks of Basic Military Training, individuals will head to Wright Patterson Air Force Base in Ohio.
The technical training will last roughly 42 days and will give airman credits towards Aerospace Physiology Technology.
What does an Air Force Aerospace and Operational Physiologist Do?

An Aerospace and Operational Physiologist is responsible for training the pilot and crew on all aspects of flight preparation and emergency planning.
During technical school, they learn the skills to be trainers, safety observers and training device operators.
Aerospace and Operational Physiologist are trained to teach pilots and staff how to correct standard operating procedures mid-flight to avoid an emergency or to adjust to an emergency.
These individuals will train airman on proper pre-flight and post-flight preparation.
The job of an Aerospace and Operational Physiologist is to ensure the overall safety of individuals on flight.
They do this by conducting lectures, discussions and demonstrations to showcase physiological stresses.
Specialist will use an altitude chamber to showcase the effects of reduced pressure and Oxygen.
This is used for flight simulation training.
Some of the other tools that these airman use to train include:
- Oxygen Masks
- Ejection Seats
- Pressure Suits
- Night Vision Goggles
- Parachutes
Any physiological issues such as decompression sickness, ear blockage or pressure issues will be evaluating by these team members.
In addition to evaluations, they will maintain the records on each of the chambers and the individual effects the chambers have on participants.
The health and safety of the participants is important and Aerospace and Operational Physiologist will monitor the equipment and personnel during all training.
Specialist can participate in parachuting activities.
Related Article – Air Force Pararescue (PJ’s): Career Details
When an Aerospace and Operational Physiologist is at an emergency, they will provide basic first aid until a medic can relieve them.
They also resolve any technical issues pertaining to aerospace and operational physiology activities.
Individuals in this position receive specialized training that allows them to be instructors on different pressure chamber types and experts in high-altitude missions.
Aerospace and Operational Physiology specialist are considered High Altitude Reconnaissance Aircraft Technicians.
Because of this title they receive training on the U-2 system (high-altitude aircraft reconnaissance).
This training is an additional 14-18 months of training on the U-2 system, that allows them to build specialized equipment just for U-2 operation needs.
The video below gives a description on what it is like in the Aerospace and Operational Physiology position.
What is the pay for Air Force Aerospace and Operational Physiology?
All enlisted Air Force members will receive the same base pay.
This base pay changes according to your rank and years of service.
You can find the 2019 pay table for the Air Force below.
| Insignia | Pay Grade | Rank | Abbreviation | 2023 Minimum Monthly Pay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-1 +4 months | Airman Basic | AB | $1,917.60 | |
| E-2 | Airman | Amn | $2,149.20 | |
| E-3 | Airman First Class | A1C | $2,259.90 | |
| E-4 | Senior Airman | SrA | $2,503.50 | |
| E-5 | Staff Sergeant | SSgt | $2,730.30 | |
| E-6 | Technical Sergeant | TSgt | $2,980.50 | |
| E-7 | Master Sergeant | MSgt | $3,445.80 | |
| E-8 | Senior Master Sergeant | SMSgt | $4,957.20 | |
| E-9 | Chief Master Sergeant | CMSgt | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Command Chief Master Sergeant | CCM | $6,055.50 | |
| E-9 | Chief Master Sergeant Of The Air Force | CMSAF | $6,055.50 |
Benefits
In addition to the base pay above, the Air Force offers many benefits that would be unavailable in the majority of civilian career fields.
Insurance and Time Off
The Air Force provides free or low cost insurance and dental.
They also provide paid sick time and 30 days paid vacation.
A generous retirement package is offered for individuals who complete 20 years of service.
The retirement package is considered generous because it is available on the day you retire and does not require a pay check deduction.
Housing and Food
For individuals who choose to live on-base, you can receive free housing expenses including maintenance and utilities.
If you choose to live off the base, you can receive a housing allowance that is based on rank, family status and location.
Airman are provided with a meal allowance.
In addition to the meal allowance, there are tax-free department and grocery stores available to help you save money.
Education
As soon as you begin with the Air Force and begin Basic Military Training, you will be enrolled in Community College of the Air Force and will start earning college credit.
As an airman you have the opportunity to get up to 100% tuition coverage with the many tuition assistance options.
These options include:
- Air Force Tuition Assistance program
- Post 9/11 GI Bill
- Montgomery GI Bill
Recreation
Living on-base or working at a base has it’s perks.
Most locations are equipped with swimming pools, golf courses, bowling alleys and many other recreational locations.
Every base organizes social activities and recreational programs.
These programs could be clubs or youth activities.
The goal of the recreation available on the base is to provide each aged member of the family with a recreational option.
Related Article – How To Join The Space Force
Job Reviews
Aerospace and Operational Physiology specialist have positions that allow them to train and ensure the security of airman.
This is not a position that generally requires a lot of travel.
Reviews indicate that people in this position are happy that they chose this job.
Not only is the job satisfying, so is being able to use all of the rewards of joining the Air Force.
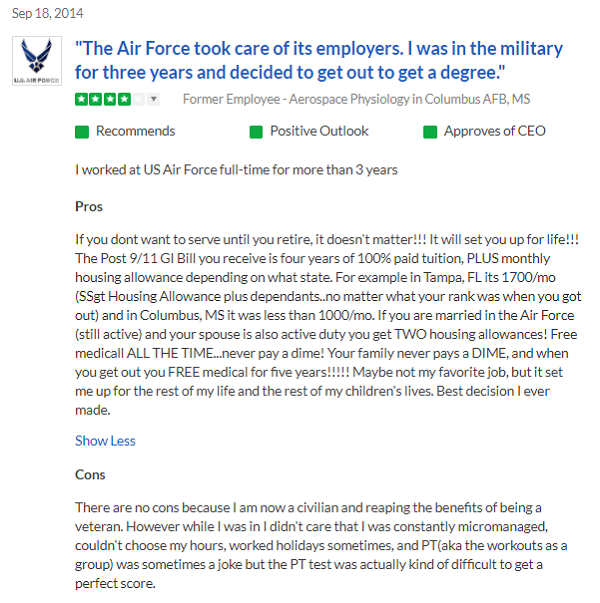
See the review from a previous Aerospace Physiologist.
Civilian Job Opportunities

Previous Air Force Aerospace and Operational Physiologist can work as a Hyperbaric Technician.
This position is responsible for oxygen therapy.
Individuals can use skills learned to work in safety as program managers or health safety managers.
The testing and documentation duties in the Aerospace and Operational matches the qualifications for a research associate for aerospace development and testing centers.
An example business for the above position would be KBRWyle in San Antonio, TX.
Working in Aerospace and Operational Physiology gives you experience in training and the medical field.
Related Article – Air Force Aircraft Loadmaster: Career Details
Conclusion
Aerospace and Operational Physiologist are responsible for the safety of pilots and crews.
They train, test and document all activities related to aerospace physiology.
To join the Air Force in an Aerospace and Operational Physiology position you have to have a High School Diploma or GED with college credits.
After you meet all requirements, you will attend Basic Training for 8.5 weeks then technical training at Wright Patterson AFB.
The Air Force offers many benefits including base pay, insurance and tuition assistance.
Enlisted individuals previously in this position express that they were satisfied with the position and the skills they learned.
There are many different career fields that Aerospace and Operational Physiology recruits can enter into in the civilian world.
Some of these fields include, safety, health and aerospace science.
References
- Ikon Pass Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big - January 31, 2025
- RTIC Military Discount: Find Out How To Save Big on Gear - January 30, 2025
- Traeger Military Discount: Learn How To Save Big on Smokers - January 28, 2025

